Technical analysis is one of the many methods traders and investors use to navigate market exchanges.
In this article, we give you a crash course on technical analysis.
We go over the basics, as well as the tools and methods used. We discover the limitations of technical analysis and we discuss the difference between Technical Analysis and Fundamental Analysis.
PS. We recently published a guide on price action trading 101.
What is Technical Analysis?
Technical analysis is one of many trading methods that are used to evaluate investments and trade opportunities. It does this by analyzing statistical trends based on trading activity.
An assumption made by technical traders is that the current and past price action is the most reliable future price action indicator within financial markets.
This trading discipline is often compared to fundamental analysis. The key difference between these is their methodology. While technical analysis focuses on a statistical analysis of market trends, fundamental analysis focuses on the company’s financials and fundamental.
Technical analysis is a great method for finding good, low-risk trades and investments. This discipline is also used when traders or investors attempt to predict price point movements of a tradable asset. The key focus is on the supply and demand of currency pairs, bonds, stocks, etc.
Researchers have identified numerous patterns and indicators that support this discipline of trading. Using these patterns and indicators as a basis, technical analysts have developed a plethora of trading systems that help them track the price fluctuations of financial assets.
Pros
- Technical analysts do not rely as heavily on fundamental data. This is because, for a technical analyst, the effects of this information have already been accounted for in the market activity in some way or the other. Because of this, technical analysts rarely wait for monthly or quarterly data to be released.
- Technical analysis data gives traders a snapshot of the data and the charting method includes all the information that they need to predict market trends. The information charts can show include the price movement, the volume, and opening interest of a financial asset.
- Technical analysts can easily estimate their potential profit targets and their risk management parameters. This helps them decide when and how to trade.
Cons
- Technical analysis strategies can sometimes be based on outdated or lagging indicators since these indicators display what happened in the past, and not what is happening in the present. Therefore, they cannot accurately predict future market trends.
- Technical tools are available to everyone. They are not exclusive to technical analysts. What this means is that technical traders are competing with traders at every experience level. Because many technical traders use similar tools, they could come up with similar strategies and this can lead to common and predictable protective stop placements and resistance and support zones. This creates price fluctuations.
- There is a steep learning curve when starting in technical analysis. Interpreting charts and calculations are difficult and traders need to learn how to be the best at it to stay competitive. The interpretation of the calculations is a key factor in technical analysis and could mean the difference between a profit and a loss.
Technical analysis assumptions
There are three general assumptions that professional technical traders and analysts make. The first assumption is that the market discounts everything. Technical traders firmly believe that everything concerning a company, including facts like the broad market and market psychology, has already been added to the price of the stock.
This belief is similar to the Efficient Markets Hypothesis (EMH). Tied to this assumption is the belief that the price of an asset is determined by the supply and demand for that asset in the market exchange.
The second assumption made is that the prices of assets will display the current market trends. Technical traders believe that the price of an asset is more likely to continue beyond a trend than fluctuate erratically. Numerous trading strategies are based on this assumption.
The third assumption is that history repeats itself. What this means is that market trends and price movements tend to be repetitive. This assumption stems from market psychology which is based on strong emotions of excitement or fear, which tend to be predictable.
Technical analysts will use chart patterns in an attempt to analyze these emotions and the effect they have on market trends.
Technical analysis methods
There is a myriad of trading systems that could be used to track the price fluctuations of financial instruments to aid technical traders in predicting future price points.
If we went through every single trading system, we would be here all day. Instead, we have listed the most common trade systems in technical analysis:
Time-frame charting:
When using time-frame charting, technical traders will analyze the price chart of a financial instrument to predict price fluctuations. The key variable in this method of technical analysis is the time-frames and the technical indicators that are used.
Popular time-frames include:
- 5-minute charts
- 15-minute chart
- An hourly chart
- 4-hour chart
- A daily chart
Traders can choose a time-frame chart that suits their style and needs. For example, day traders might value the information gained from the 5 minute or 15-minute time-frame charts while a trader who has long-term aims might value the daily chart.
The Candlestick method:
The candlestick method of charting is used to show the price point fluctuations on a chart. This method involves forming a ‘candlestick’ from the price action at every time frame for a single period.
This method involves drawing ‘candlesticks’ on the asset’s price chart. The highest point on the candlestick corresponds to the highest price that an asset is valued at during a given time. The lowest point of the candle corresponds to the lowest price an asset is valued at during a given time.
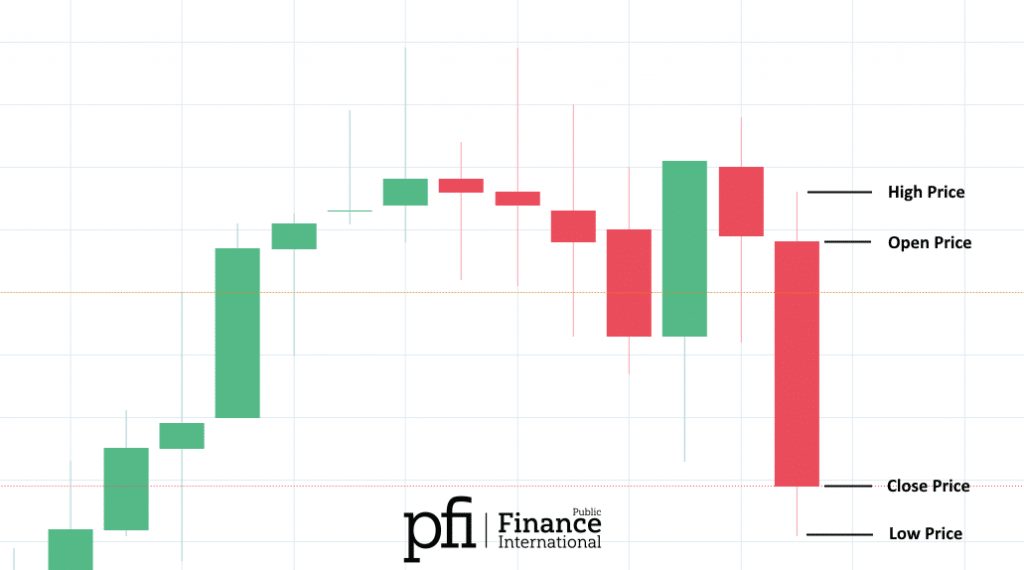
The body of the candle represents the opening and closing points for the given time. This is usually indicated by thicker blocks on the body.
The candlestick method packs the data of multiple time-frames into simple, single price bars. This format is useful because it makes the process of data analysis simpler. The candlestick method generates patterns that traders can use to predict price point movements.
What makes the candlestick method so great is that traders can color-code the ‘candlestick’ indicators which can add an extra layer of depth to the analysis. It doesn’t hurt that it’s pretty to look at either. By having color-coded candlesticks, traders are easily able to compare the opening and closing prices of an asset to the highest and lowest price points of that asset.
While this method might seem amazing, we would advise that you approach with caution as the candlestick patterns might not always be reliable, particularly in the contemporary world of electronics.
The false breakout method:
The false breakout method uses false signals in trading strategies as a method of predicting market fluctuations. In simple terms, this technical trading method uses the ‘mistakes’ of your trading strategy as an additional means of predicting market trends.
A false breakout is any move that occurs above resistance or below support. This move is then followed by a reversal that fails to act as new support or resistance for the broken level.
The false breakout method is quite popular among momentum traders who see the false signals as an indication of changes in market trends and the start of a new tread.
Technical trading indicators
In this section, we will be presenting popular technical trading indicators. Technical trading indicators are pattern-based signals that are generated by the open interest, value, volume, or contract of the asset or security that the trader uses.
Technical traders often use trading indicators to analyze historical data to make predictions on market trends and price fluctuations.
Here are a few popular technical trading indicators:
Trend indicators
Trend indicators aim to help traders trade currency pairs. A trade indicator is great for identifying the direction of a trend.
Traders can use trend indicators in an attempt to isolate and extract profits from these trends. Trend indicators attempt to capture gains by analyzing the momentum of an asset in a specific direction.
The moving average indicator
The moving average indicator (MA) is a technical trading tool. The MA works by averaging a currency pair’s value over some time. This method has a smoothing effect on the time-period chart. This makes it easier to read the chart and gives a clearer indication of which direction the pair is moving.
There are various types of moving averages but the most common are the Simple Moving Averages and the Exponential Moving Average.
The MA is illustrated by a line drawn on the time-period chart. This line is used to measure the mean value of an asset pair over some time.
Traders can use the MA to predict market trends.
A downside of this method is that it is slower to react to ever-changing market conditions. It is also not suitable for traders working on shorter timeframes.
Oscillator indicator
Oscillator indicators are used by traders when they want to gauge the momentum of a currency pair. As the price goes up, the oscillator will also move up. When the price drops, the oscillator will drop.
Once the oscillator reaches an ‘extreme high’ this might indicate that the price will drop back to the average value. Oscillators generally stay at extreme highs for extended periods and therefore, it is better to wait for a viable sign of change before you decide to trade.
Oscillator indicators can also be used to predict the breaking point in price fluctuations. On the chart, this will be displayed as the lines moving in the same direction and the price. However, once the lines move apart, the trend is believed to be losing momentum.
Oscillator indicators are quite popular among technical traders since they indicate trends and offer insight into the momentum of the market.
However, like any other indicator. This method isn’t foolproof and false signals do occur.
Ichimoku indicator
This is a Japanese indicator. Unlike the other indicators on this list, the Ichimoku was designed to be used on its own. This indicator shows current market trends and shows the levels of support and resistance.
This indicator is great because it shows when a trend is likely to be reversed.
ADX indicator
Unlike the other indicators on this list, the Average Direction Index indicator does not show price fluctuations and instead, shows traders when the price of an asset is ranging or trending.
The ADI is a great indicator for a range or trend trading strategy where traders are executing trades based on market conditions.
Pivot indicator
Pivot indicators, also known as daily pivot indicators, are used to identify numerous resistance and support levels as well as the pivot point. Traders often use this indicator to identify the price levels of an asset before opening or closing out of trades.
If the daily pivot indicates that trading has increased or decreased significantly, this is usually interpreted as a ‘breakout’ trend. Technical analysts then assume that this will cause market prices to rise significantly or drop significantly, depending on the direction of the breakout.
Fibonacci Retracements
The Fibonacci retracements are a continuous series of patterns. Fibonacci retracements are indicators that are aimed at finding support and resistance levels on a trading instrument. This indicator works on the assumption that markets react or retrace by smaller portions of larger movements and that it is possible to predict these smaller portions.
This indicator plays a key role in forex trade evaluations and has a long history within forex trading.
However, a downside to this method is that, unlike other indicators on this list, the Fibonacci retracements entail subjective evaluations. This means that technical traders might be influencing price fluctuations based on their trade exchanges.
The limitations of technical analysis
A key criticism of technical analysis is that analysts believe the EMH is evidence of the lack of actionable information displayed by historical prices and volume data. However, this stance has been criticized because, by that reasoning, business fundamentals shouldn’t provide any actionable information either.
Another criticism is that the assumption of ‘history repeats itself’ is not entirely accurate. It is argued that this method of studying price patterns has inflated importance and should not be taken seriously.
Critics also argue that technical analysis seems to work based on a self-fulfilling prophecy. What this means is that technical analysts might be influencing the market with the trade executions in ways that cause their predictions to be fulfilled.
For example, suppose around 100 technical analysts decide to place a stop-loss order below the 200-day moving average of a company. In that case, there will be a high number of sell orders and this will push the price of the stock down, which will be exactly what the technical traders expected would happen.
These actions merely reinforce their assumptions but have little meaning in the long-term price movements of an asset.
The differences between Technical Analysis and Fundamental Analysis
Technical analysis and fundamental analysis are major schools of thought in the world of finance and trading. They are two vastly different methods of approaching market exchanges.
The common factor is that they are both used as a method of researching and predicting market trends and price fluctuations.
Fundamental analysis differs from technical analysis because it aims to evaluate financial assets and securities by measuring the intrinsic value of the asset or security. Fundamental traders analyze everything that has to do with the asset. This includes the state of the economy and industry and the financial condition and management of the company.
Fundamentalists also analyze the expenses, earnings, assets, and liabilities of a company to predict market trends.
This is vastly different from technical analysts who only consider the volume and value of an asset. This is because technical analysts act under the assumption that all known fundamentals have already been factored into the value of the asset. Therefore, it would be unnecessary to consider them.
In Summary
Technical analysis is a school of thought that has given rise to multiple trading strategies. Technical analysis aims to analyze the price and volume of an asset to predict market trends and price fluctuations.
It works based on three assumptions, namely; history repeats itself, fundamentals are already accounted for in the value of financial assets, and prices will exhibit market trends regardless of erratic market fluctuations.
These assumptions underlie the technical indicators used to predict market trends. Technical indicators are used as analysis methods and are displayed on comprehensive charts. Technical indicators are generally based on historical data.
Technical analysis has often been criticized for its lack of consideration regarding market fundamentals such as the state of a company and the market climate. It has also been criticized for its reliance on historical data instead of present-day data when predicting market trends.
However, despite these critiques, technical analysis remains a popular ideology when developing a trading strategy and many traders swear by it.